Last Updated on 2 years ago by
The criteria used by Google (and other search engines) when reviewing sites to determine the optimal order of relevant results to provide for a search query are known as ranking factors.
Understanding low Google ranking elements is essential for SEO success. All digital marketing professionals, including SEO agency professionals, are extremely sensitive to these ranking factors. Not because they’re the be-all and end-all of SEO (they’re not), but because they help create a better user experience, which leads to more leads and conversions for your company. A decline in ranks can be caused by several factors. This page explains both the apparent and less obvious ones. Here are 16 low Google ranking factors:
You Are Busy Creating Lots of Low-Quality Links to Your Site
A low-quality link is one that was manufactured or acquired to manipulate PageRank and has a direct influence on a low Google ranking in the search results. Low-quality links come from low-quality web directories, low-quality article directories, low-quality guest posts, or spam comments. These are all examples of low-quality links.
-
How To Identify Low-Quality Links

Look for site messages under ‘Search Console’. If your site has a lot of artificial links going to it, Google is likely to give you a notice directly requesting that you address those connections. It doesn’t imply you’re out of the woods just because you haven’t gotten any direct communication from Google.
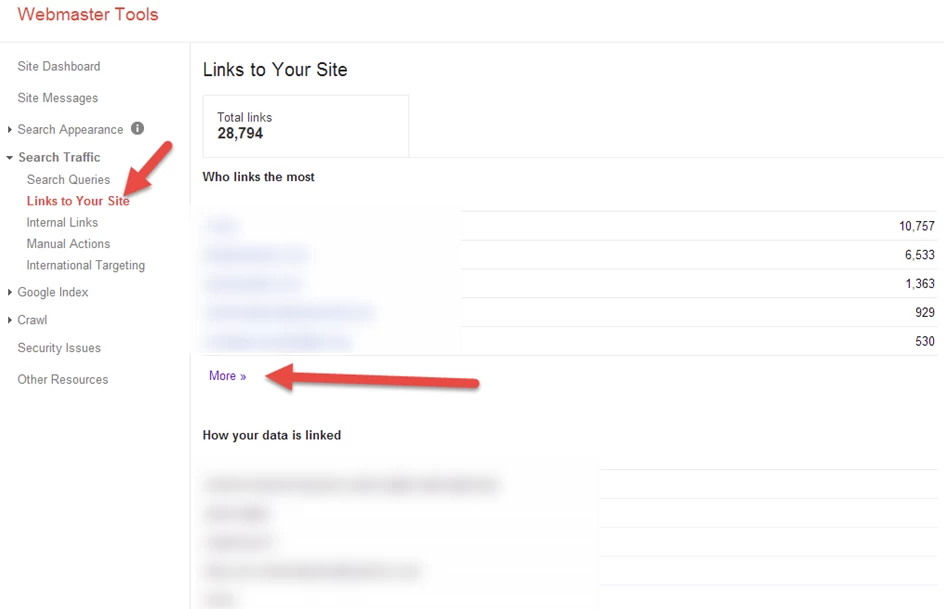
If you’re aware that your site has low-quality links, you should investigate them. Log in to the Search Console and go to Search Traffic > Links to Your Site. Download the list and remove any sites with low authority, low Google ranking, or a high spam score. You may also go over each link and filter out any artificial links depending on the type of link scheme.
-
How To Fix The Problem Of Low-Quality Links
Once you’ve found a list of low-quality URLs connecting to your site, try to get those links removed by writing an email to the webmaster and asking them to do so. Please allow at least 6-8 weeks for the procedure to send and receive answers to emails.
Take screenshots of emails you send to the webmasters at this time. You can disavow all of the low-quality links that are still visible. Once the procedure is completed and the problem has been resolved, submit a reconsideration request to Google. Also, note that you may only make a reconsideration request after receiving a manual penalty.
Bad Redirects Causes Low Google Ranking
When a visitor accesses a URL and is redirected to another URL, this is known as a redirect. Consider the following scenario: You have a page on your site called www.example.com/SEO-agency that ranks top on Google.
Every month, the page attracts roughly 10,000 unique visitors. The developer redirects that URL to the main page www.example.com due to certain modifications in the website design. This is a poor redirect because it does not satisfy the user’s objective. The visitor is seeking an SEO agency, however, the freshly redirected page has very little information about them. As a result, the content was virtually modified, and the URL’s ranks were lost.
-
How To Identify Bad Redirects
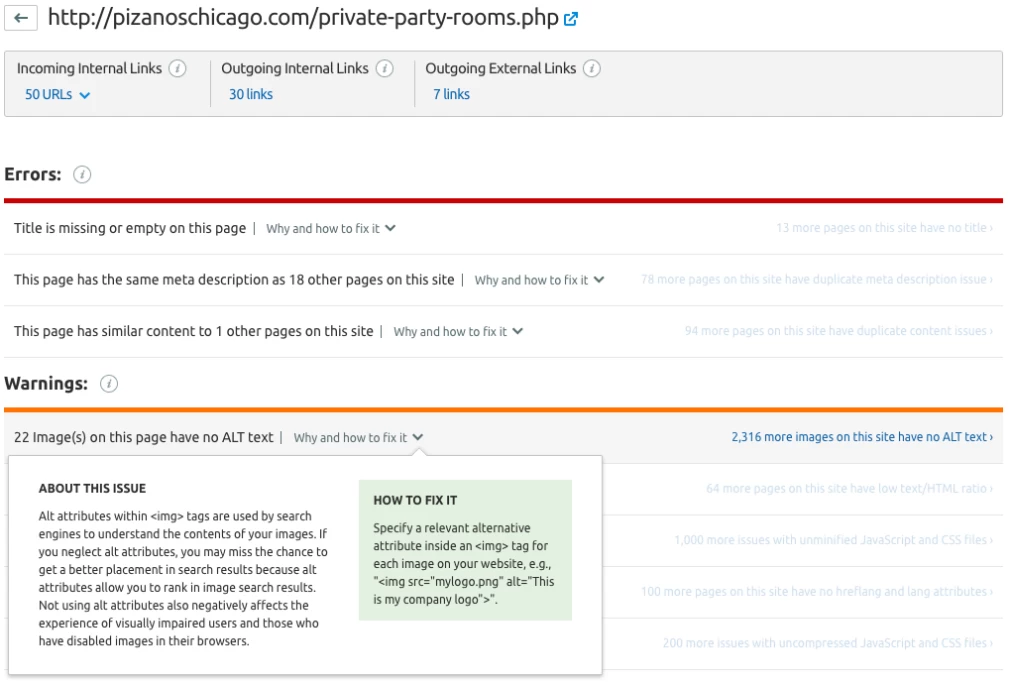
Export all of the landing pages that are ranked in organic search using Google Analytics. Then, in Screaming Frog, paste the list of URLs by selecting mode > list > paste. You’ll be able to see all of the problematic redirects, including ones that go to 404 pages or the home page.
-
How To Fix Bad Redirects
You’ll need to construct an alternate URL for each new redirect once you’ve compiled a list of URLs. Users should be sent to a new page that has the same (or better) content as the previous page. If your pages aren’t ready yet, there’s no need to use redirects.
You must not alter the old URL until your new page is complete. Always keep in mind that each new page must always meet the user’s objective. If you generate a lot of redirects that go to the homepage or another page with content that isn’t the same as the original page, the diverted page’s rankings will suffer.
Duplicate Content Causes Low Google Ranking
Duplicate content is defined as substantial blocks of content inside or across domains that are either identical to or substantially similar to other content. If you’ve just updated your site’s content and a significant percentage of it is duplicated, it might cause a low Google ranking.
If you’ve added new pages to your site and the content on those pages is mostly identical to the information on other pages on your site (including the title or H1 tags), it might be deemed duplicate content.
-
How To Identify Duplicate Content
Use SEO tools to discover duplicate content on your site. If this tool bot finds numerous pages with 80% content similarity, it will flag them as duplicate content. Furthermore, pages with insufficient content may be considered duplicate content.
-
How To Fix Duplicate Content
When you build new pages, use 301 redirects so that search engines and people can’t find the old ones. Similarly, for pages with similar content, use rel=canonical tags to let search engines know which information should be recognized as original. Remember to use rel=noindex for pages that aren’t ready yet, and aim to keep the amount of boilerplate text on your site to a minimum.
You Have Recently Updated Your Title Or Meta Tags
Because it allows Google to comprehend the contents of your web page, the title tag is an incredibly crucial aspect of your on-page SEO. As a result, even minor changes in the title tag might cause a low Google ranking.
For example, if your homepage’s title tag is ‘SEO Agency’ and you alter it to ‘Hire A SEO Specialist’ your rankings for keywords like ‘SEO agency’ may suffer as a result of the term ‘agency’ being removed from the title tag.
-
How To Confirm
Enquire with your web developer about any modifications he may have made to the page’s meta tags. Log in to Google Analytics and export all of the organically ranked landing pages.
Use a web crawler like Screaming Frog to swiftly scan all of your sites that rank in organic search for new meta tags. Compare the title and meta tags to the previous backup of your website. Add a column for old meta tags to the list of URLs with new meta tags.
-
How To Fix It
You may repair the problem by rewriting the new titles and meta tags and replacing them with the old ones. You may also re-crawl the website by including the missing keywords in your new title tag. This might help you reclaim your lost ranks.
You Have Recently Made Changes In Content
If you make any modifications to your site’s content, especially H1s, you may see a low Google ranking. Content is an important ranking component, and all web pages are ranked based on it. Any changes are likely to trigger a shift in rankings.
-
How To Confirm
Log in to Google Analytics and export all of the organically ranked landing pages. Request a backup of your website from your web developer. Compare the content changes for each URL and make a list of the ones that have changed. This project will take a long time to complete. There are solutions like OnWebChange that will inform you of any changes to the website design or content, which may save you time.
-
How To Fix It
Once you’ve compiled a list of URLs to update, you can either rewrite the content from an old backup or ask your SEO to incorporate the missing keywords into the new text. This technique will have the least amount of negative influence on lost rankings. If you are unable to locate a copy of your website, you can utilize the Way Back Machine to retrieve your website’s backup history.
You Have Incorrectly Used Noindex tag, Robots.txt File, and Nofollow Attribute
Webmasters frequently overlook several critical technical concerns that might have a significant influence on high or low Google ranking. The inappropriate use of the noindex tag, robots.txt file, and nofollow attribute are three of these concerns.
For example, your web developer may have accidentally included a no-index tag on one of your critical sites that ranks well in search results. What was the result? The webpage is no longer visible in the search results. A similar scenario may happen with robots.txt, where a single line of code might prevent search engines from crawling your site, causing all of your site’s rankings to plummet all at once. On the other hand, a nofollow attribute applied to your site’s internal pages will have a direct influence on PageRank and cause your site’s ranks to plummet.
-
How To Check
If you’ve noticed a decline in ranks across the board, examine your robots.txt file to see if you’ve accidentally blocked search engine crawlers from seeing your site.
Check the noindex or nofollow attributes by right-clicking on the page and reading the source code if you observe a drop in certain of your web pages. The existence of a noindex tag on a page will have the same effect as a robots.txt exclusion, but the presence of a nofollow attribute on any internal links will limit the flow of link juice and result in a decline in the ranks.
-
How To Fix It
Change the text of your robots.txt file as soon as possible, and delete any links that prevent search engines from accessing pages on your site that are critical for organic search visibility. Similarly, look for any instances of noindex or nofollow tags in the source code and delete them right away.
Your Site Is Getting Lots Of Low-Quality Traffic
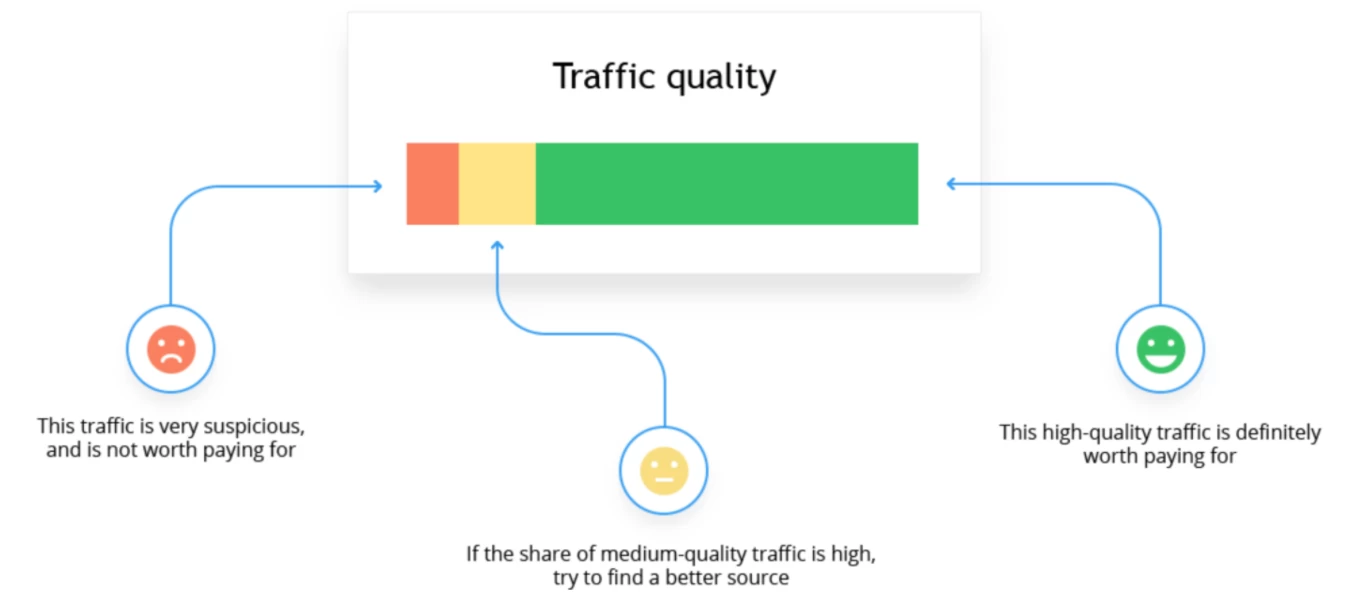
Low-quality traffic does not immediately harm your site’s ranking, but it might have an indirect effect on low Google ranking. If you discover that your site is receiving a lot of low-quality traffic, you may be acquiring connections from low-quality directories or irrelevant sites via purchased links or bad SEO; this can have a direct influence on conversions, time on page, bounce rate, and other metrics. All of these criteria together will signal to Google that consumers dislike your website, potentially resulting in a low Google ranking.
-
How To Identify Low-Quality Traffic
You may use a program to assess traffic quality; it will help you identify particular IP addresses and domains that are sending undesirable traffic to your website. Finteza can recognize up to 12 different forms of malicious traffic, including bots.
-
How To Fix It
After you’ve narrowed down the sites that are sending you low-quality traffic, be sure to remove your links/ads (even if they’re nofollow) from them. Remember that some links may be nofollow, and the only method to filter out such sites is to use traffic quality monitoring.
Google Has Made A Recent Update To Its Ranking Algorithm
Updates to the core algorithm are an unavoidable component of the entire search process. There’s a potential that your website’s rankings will change whenever such upgrades occur (which might happen many times a day, and Google may not explicitly mention such revisions). A low Google ranking as a result of a Google update does not always imply that something is wrong with your site.
-
How To Confirm The Update
Keep an eye on the Google Webmasters Blog for updates. If a large algorithmic upgrade harms some sites, Google will usually disclose it and offer instructions on how to adjust your site. If Google doesn’t make a statement, you may fairly conclude that the shift in ranks is due to core upgrades. The only thing you can do when a core change occurs is improve the user experience. If your consumers enjoy your site, Google will most certainly like it as well.
-
What Should Be Your Next Step
Create a Google alert for any Google updates and follow reputable SEO sites such as Search Engine Land, Search Engine Roundtable, Search Engine Watch, and others. These blogs are excellent resources for learning all there is to know about SEO and search engines.
You Have Violated Copyright Knowingly or Unknowingly
Your rankings will decline if your site receives a large number of genuine copyright takedown notices. Sites with a significant number of removal notices may show a low Google ranking. This ranking tweak should make it easier for people to access real, high-quality content. Copyright infringement can take many different forms. If you carry out the following acts without first receiving permission from the owner, author, or holder of the copyrighted content, you will be committing copyright infringement:
- In a cinema theater, recording a film
- Using copyrighted songs from a musical group on your company’s website
- Changing a photograph and putting it on your business’s website
- Creating products using copyrighted text or pictures for sale
-
How To Identify Copyright Violation
Enter your website URL into the Google Transparency Report to discover the number of requests made against it by others.
-
How To Fix It
Remove the pages that invite copyright infringement as soon as possible, and make sure there are no further copyright infringements on your part. Copyright infringements might occur in the form of text, pictures, audio, or video. It’s best to keep an eye on the transparency report and implement a rigorous content policy that prevents copyright content from being published on your site.
There Is a Rise In Local Competition

The growth in local competition can have a detrimental effect on low Google ranking. Let’s say you have a bakery in LA and there are no other bakeries in the vicinity. It will be easy for you to maintain your position in local search results. However, if two new bakeries pop up in LA, your competition will increase, causing a drop in the rankings. Another example is when a former LA baker suddenly opens a new Google My Business account and invests in internet marketing to outrank you in local search results.
-
How To Identify Competition
One method is to use Google to search for your core company keywords and see who your rivals are. SEO tools may also help you locate new online competitors, learn what keywords they rank for, and watch your rankings so you know when a competitor takes over your position.
-
What Should Be Your Next Step
Once you’ve found your new rivals, use a competitive research tool to keep track of their efforts so you can see any gaps in your SEO approach. If you want to beat your emerging opponent, you may need to raise your link-building expenditure.
Your Site Is Not Mobile Friendly And Not Ready For Voice Search

Mobile pages that deliver a bad search experience can be downgraded in rank or shown with a warning in mobile search results, according to Google. When it comes to finding important information, people are increasingly turning to their cell phones. Mobile devices now account for up to half of all searches.
Google may penalize a website that is not mobile-friendly. Google is continuously searching for ways to improve the user experience. A responsive website is the first step toward that objective. As a result, Google has shifted to a mobile-first index. This means that websites are now ranked primarily on their mobile version of content rather than their desktop version.
Voice search and mobile sites are inextricably linked. If you still don’t have a mobile-friendly, responsive website, you’re likely to lose your existing search rankings.
-
How To Check Mobile Friendliness
Take the mobile-friendly test to see if your website is mobile-friendly. The Google test will quickly and efficiently examine the URL of your site to see if it is mobile-friendly. Since Google now considers mobile design when evaluating websites, you may wish to use this tool if you’ve observed a drop in your Google rating. This tool shows you how Google perceives your website, and whether it’s mobile-friendly, you’ll know straight away. If it isn’t, you may take the required actions to make it better.
-
How To Fix It
When you take the mobile-friendly test, Google will immediately advise you on the improvements you should make to your website. Request that your developer make the adjustments or make your website responsive so that users may view it regardless of the device they’re using. Optimize your website for voice search (particularly for question keywords) as well; this will aid in the development of your future site.
Negative SEO Causes Low Google Ranking
Negative SEO is a collection of tactics aimed at lowering a competitor’s website’s search engine rankings. Creating spammy, artificial links to the site, content scraping, and even hacking the site are examples of these practices.
Negative SEO occurs when your competitors attempt to degrade your ranks by employing unethical tactics. Your competition could destroy your rankings by employing black hat SEO techniques.
-
How To Identify
Negative SEO can be identified in several ways:
- Keep track of how many links you’re getting. If you notice a lot of links coming from low-quality sites that you didn’t develop, your competition is likely doing it for you.
- Check the robots.txt file, .htaccess file, and the Search Console for any problems, warnings, or malware regularly.
- Use tools like Copyscape to find out whether you’ve been a victim of content scraping.
- Keep a watch on the traffic quality, particularly if the number of bots or bounce rate increases.
- Check your site’s performance and address any issues that are slowing it down.
-
How To Fix It
Fix all of the problems you found in the previous phase. You should keep an eye on your website using Search Console regularly. Keep a watch on the links you’ve acquired or lost, since this is the most common reason for bad SEO to lead you to drop in ranks. Maintain a malware-free website, and keep a copy of your most recent backup on hand in case of an emergency. A single piece of malware may cause your site’s rankings to plummet nearly instantaneously.
Your Site Has Suddenly Become Unsafe
If you want to rank well, Google needs to trust your site. Site security is critical from the minute you decide to develop a website. When it comes to crawling and indexing content, having a safe and trustworthy site makes things a lot easier for Google. Keep in mind that Google favors sites that are simple to navigate.
If Google finds that your site has been hacked or infected with malware, you’re in big danger since Google will quickly lower your ranks. Internet safety is a major problem that Google takes very seriously since it directly impacts children. In this instance, Google may provide a cautionary message in the search results.
-
How To Check For Malware
Visit the Search Console right away and look for any Google messages. In most circumstances, Google will send you a notification stating that your site has been hacked. You may also use the Safe Browsing tool to examine your site for any concerns.
-
How To Fix The Issue
Google will advise you on the steps to take to ensure that your website is malware-free. These methods will be provided in the Search Console’s messages area. If you’re still having trouble, the best thing you can do is submit a backup of your site and request a review.
You Have Lots Of Links Pointing To Other Sites

A high number of connections from places often employed by black hat SEOs (such as blog comments and forum profiles) might indicate that you’re trying to game the system. Your site may low Google ranking if it has a lot of links leading to low-quality, spammy sites. The reason for this is that it is against the Webmaster Guidelines.
-
How To Identify Low-Quality Links Pointing To Other Sites
Check for messages in the Search Console by logging in.
-
How To Fix It
It is necessary to delete all unnatural links from your site that Google may interpret as dishonest and fake. The anchor text of the links, the spam score of the domains you’re connecting to, and the niches of the sites you’re linking to are all important factors to consider. Remove any spammy or irrelevant links right away.
You Have Recently Changed the Internal Linking Of Your Website
Internal links are any links on your website that connect one page to another. Links are used by both your users and search engines to discover content on your website. Users utilize links to browse through your site and discover the information they’re looking for. Search engines utilize links to navigate your site as well. If there are no links to a page, they will not see it.
Any alterations to the internal linking structure might result in a significant decline in search rankings. For example, suppose you have 1000 internal links from the main menu heading to a high-ranking inner page. Assume you delete the navigation link, which results in a loss of 1000 internal links; this significant change will gradually cause the page’s search rankings to drop.
-
How To Check And Fix It
The Google Search Console is the best spot to see whether you’ve lost numerous internal links pointing to any of your critical sites. Navigate to Links in the Search Console after logging in.
You’ll be able to see your site’s top connected pages here. Download the data and check for any recent 404 errors that may be causing a decrease in the number of internal links.
You Recently Added Lots of Pages On Your Site with Low-Quality Content
Pages with little content (such as attachment pages in WordPress that are used as placeholders for images), pages with duplicate content, or pages with poorly written content are all examples of low-quality web pages. These pages are low-quality since they don’t add anything to your rankings or give any value to your visitors. If you realize that your website has one or a few low-quality pages, here’s what you can do to fix them.
A legitimate explanation for the ranking decline might be low-quality content. If you see a sudden decline in the ranks and you know you’ve added new pages to your site, the dip may be due to low-quality content.
-
How To Identify Low-Quality Content Pages
If the following conditions apply to a page, it is considered low quality:
- The content isn’t unique or original.
- The website does not adequately respond to the user’s query.
- Relevant and authoritative sources are not cited to back up the information.
- With a lot of boilerplate text, the word count is too low.
- The language employed is difficult to comprehend.
- The page is just a replica of a concept that has previously been published on the internet.
-
How To Fix Low-Quality Content
Request a list of URLs that were recently added to your site from your developer, and go through each one carefully. Revise your content to make it more original, appealing, useful, authoritative, and simple to comprehend. Make the modifications one at a time and use the Search Console to request that the page be indexed. You’ll have to decide what the best course of action for these pages is based on their state. Consider if you still require these pages and what their general function is. From then, you have the option of doing one of the following:
- Delete the pages: If you don’t need these low-quality sites and they don’t provide any value to your SEO or visitors, you can just delete them and let Google figure out what the 404 error message means (speaking of that, we just redesigned ours). Google will be able to focus on your more relevant sites as a result of this. If this URL does receive a lot of traffic, redirecting them to a related page, article, or category could be a good idea.
- Noindex: Your low-quality pages may include useful connections to other parts of your site and help consumers go from one high-quality page to the next. If this is the case, set the robot’s meta tag to noindex. That way, Google will be able to discover this website, follow the links on it, and keep it off of the search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Rewrite the content: This is the most time-consuming choice of all. If visitors need to find this page, but the page is considered low quality, remove the content. Then replace it with new, unique, valuable, and fun information.
We would also like to point out that you could work with a content agency if you always want to create SEO-compatible content and have your content increase your website’s rankings.












